The first Certificate of Entitlement (COE) bidding results for April 2025 have sparked notable discussions in the Singapore automotive market. As the country continues to navigate various economic challenges, these bidding results offer an insightful glimpse into the shifting dynamics of the vehicle market.
With varying results across the different COE categories, understanding these changes is critical for potential car buyers, industry players, and anyone keeping a close eye on the automotive sector.
In this article, we will delve into the key takeaways from the April 2025 COE bidding results, analyze the factors driving the trends, and provide actionable insights for consumers and stakeholders in the Singaporean automotive industry.
Overview of the April 2025 1st COE Bidding Results
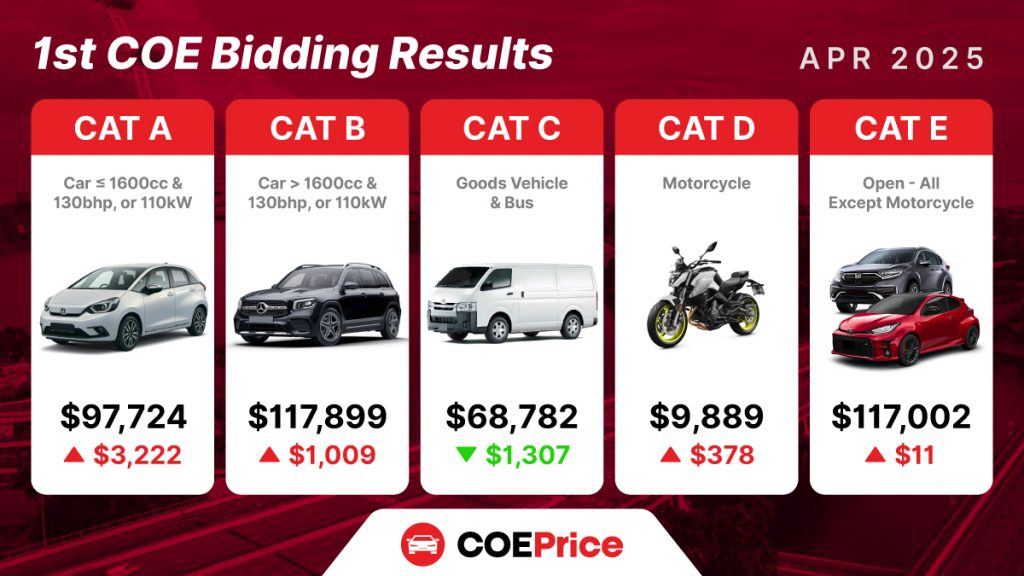
Category A (Cars ≤ 1600cc)
Analysis: The significant rise of $3,222 in COE premiums for Category A vehicles suggests a sharp demand for affordable, fuel-efficient cars. This trend can be linked to a growing preference for smaller vehicles amid rising fuel costs and government sustainability initiatives. Additionally, the tariff situation could drive up the cost of imported smaller cars, making them more expensive and further intensifying competition for COEs.
Factors Driving Trends:
- Increased demand for compact cars due to rising fuel prices and economic conditions.
- Government incentives for electric vehicles could boost interest in smaller, greener cars.
- Tariffs on car imports might affect the availability of affordable models, leading to higher COE bids.
Category B (Cars >1600cc)
Analysis: The more modest rise of $1,009 in Category B premiums indicates a steady demand for larger vehicles. Buyers in this segment are less price-sensitive and are likely seeking more powerful, spacious options. However, with tariffs affecting the prices of larger imported cars, this could increase their total cost, making COEs more expensive as buyers factor in higher vehicle costs.
Factors Driving Trends:
- Steady demand for luxury and larger cars.
- Tariffs impacting luxury car imports might lead to price hikes, indirectly pushing up COE premiums.
Category C (Goods Vehicles and Buses)
Analysis: Category C premiums have remained stable, suggesting that the demand for commercial vehicles is more closely tied to long-term business needs than to economic cycles. Despite global tariffs, which may affect the price of commercial vehicles and raw materials, the price of COEs in this category tends to remain steady, driven by consistent business demand.
Factors Driving Trends:
- Stable demand for commercial vehicles focused on business operations rather than consumer preferences.
- Supply chain disruptions from tariffs may affect vehicle availability but are less impactful on COE premiums in this category.
Category D (Motorcycles)
Analysis: Motorcycle premiums remained largely unaffected, indicating that demand for motorcycles is more consistent and less influenced by macroeconomic conditions. The impact of tariffs on motorcycle prices is also less pronounced compared to cars, as many motorcycles are manufactured locally or in countries with fewer trade barriers with Singapore.
Factors Driving Trends:
- Stable demand for motorcycles driven by their affordability and practicality.
- Minimal impact from tariffs as motorcycles often have fewer international trade constraints.
Category E (Open COE)
Analysis: The 2% increase in premiums for Category E suggests a growing interest in flexible COE options that allow for a broader range of vehicle types. As tariffs push up the cost of specific vehicle categories, buyers may turn to Category E for more options. However, as the open category is impacted by broader market trends, rising COE prices could encourage more competition for these flexible entitlements.
Factors Driving Trends:
- Increased demand for flexibility in vehicle choice due to shifting consumer preferences.
- Tariffs affecting certain vehicle categories may push buyers toward the open COE category to obtain a more adaptable entitlement.
Will Current Tariffs Affect COE Prices?
The ongoing global tariff situation, particularly between the U.S. and major economies, could influence COE prices indirectly. Higher tariffs on automotive imports might lead to increased costs for car manufacturers, which could ultimately push vehicle prices higher.
Since COEs are awarded through bidding and are influenced by vehicle demand, any rise in car prices due to tariffs could trickle down, resulting in higher demand for COEs. As vehicle prices increase, buyers may compete more fiercely for COEs, driving premiums higher.
Conclusion
The April 2025 COE results highlight several key trends in the Singapore automotive market, with each category reflecting distinct shifts in demand and vehicle preferences. While tariffs have a more significant impact on vehicle costs, the overall effect on COE prices will depend on how manufacturers adjust to these changes and whether buyers’ preferences shift accordingly.
The ongoing tariff disputes may push prices higher, causing increased competition for COEs, especially in categories where vehicles are subject to higher import costs.